Your monthly health check: Vitamin D and the sun

As part of a new partnership with Super Wellness, the University’s Occupational Health and Wellbeing team is delighted to introduce a new series of monthly check-ins with your health. Each edition revolves around a specific theme.
This month, we’ll be looking at Vitamin D and sun health.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin produced by UV radiation from sunlight as it strikes the skin. It can help with both immune and bone health, as well as improving your mood.
Our levels of Vitamin D can be affected by various factors: age, skin colour, weight, and the time of year can all play a part.
For example, the older you are, the less able your skin will be to make Vitamin D. And if your skin is darker, you’ll typically need more sun exposure to get a sufficient level of Vitamin D.
What’s a healthy level of Vitamin D and what can help me achieve this?
Ideally, you should be striving for levels above 50nmol/L. Those with 25nmol/L or below are categorised as deficient in Vitamin D.
For those who are interested, you can test your Vitamin D levels by purchasing a home kit from an NHS laboratory. More information can be found here.
To achieve a substantial level of Vitamin D, you can try the following:
- Eating Vitamin D rich foods: Examples include red meat, oily fish, eggs, and fortified foods such as cereal
- Exposure: Between March and September, most people should be able to get all the Vitamin D they need from sunlight.
- Supplements: Between the months of October to February, it is recommended to take supplements when sunlight is minimal.
Using sunscreen
Did you know that sunscreen actually reduces Vitamin D production? It’s really important everyone uses sunscreen, however you may want to consider applying it a few minutes after being exposed to the sun.
Below are some useful tips to help you understand what the various words, numbers, and ratings mean that are associated with sun cream:
- Sun Protection Factor (SPF) can block UVB rays but not UVA. The numbers can range between 2-50+. For a good standard of protection, opt for at least SPF30.
- The UVA seal accompanied by a star rating indicates the product conforms to EU recommendations for UVA protection. It’s recommended to choose one with at least four stars.
- No sun cream is 100% waterproof or sweatproof, so always reapply after swimming or exercising. It’s recommended sunscreen is reapplied every two hours, and roughly 1tsp is used per body part.
- When choosing a sun protection product, purchase one with both UVA (associated with ageing) and UVB (associated with burning) protection.
- If you have sensitive or acne-prone skin, a mineral/more natural sunscreen such as titanium oxide or zinc oxide may be more suitable for you.
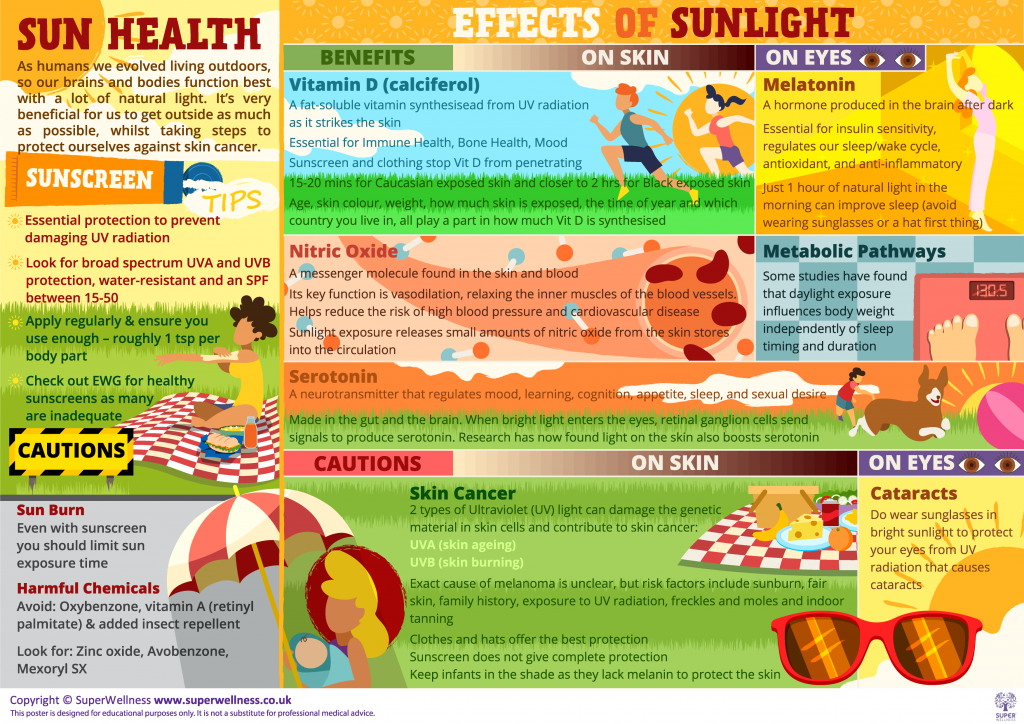
For more information about sunlight and the effects of it on the body, check out Super Wellness’ poster below. If you are experiencing any issues reading the content, please use the ‘zoom in’ tool on your browser.
Health and Wellbeing
Wellbeing means being in a positive physical, social and mental state. Wellbeing is important to us as happy, healthy people who achieve harmony in their work / life mix are more creative, productive and help to create a great place to work.